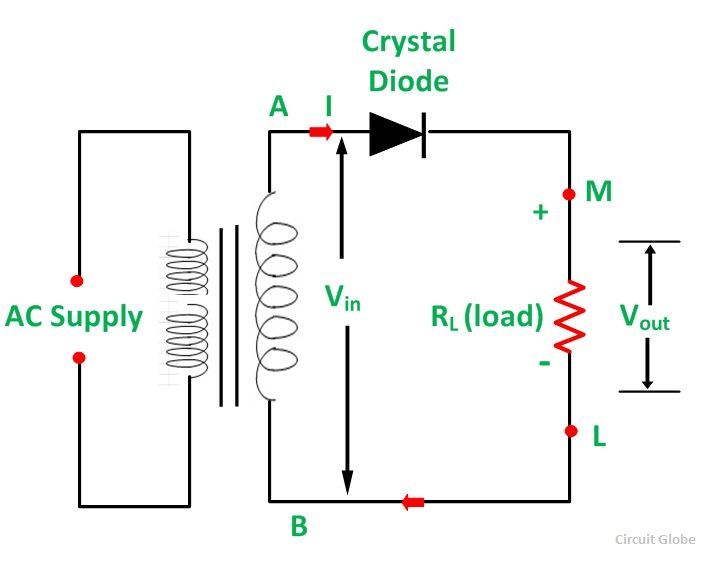
A Full Wave Rectifier is a circuit, which converts an ac voltage into a pulsating dc voltage using both half cycles of the applied ac voltage. It uses two diodes of which one conducts during one half cycle while the other conducts during the other half cycle of the applied ac voltage.
A short video here explains the working of full wave rectifier.
The circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier along with its input and output cycle.