Kirchhoff’s Laws
Kirchhoff's first law
This law is also known as junction rule of current law (KCL). According to it the algebraic sum of current meeting at a junction is zero i.e. ∑i = 0.
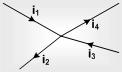
In a circuit, at any junction the sum of the currents entering the junction must equal the sum of the currents leaving the junction. i1 + i3= i2 + i4
This law is simply a statement of "conservation of charge".
Kirchhoff second law: This law is also known as loop rule or voltage law (KVL) and according to it "the algebraic sum of the changes in potential in complete traversal of a mesh (closed loop) is zero", i.e. ∑V = 0
(i) This law represents "law of conservation of energy".
(ii) If there n meshes in a circuit, the number of independent equations in accordance with loop rule will be (n –1).
Sign convention for Kirchhoff's law: For the application of Kirchhoff's laws following sign convention are to be considered
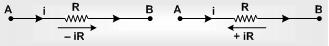
(i) The change in potential in traversing a resistance in the direction of current is –iR while in the opposite direction + iR
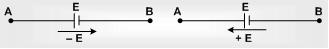
(ii) The change in potential in traversing an emf source from negative to positive terminal is +E while in the opposite direction –E irrespective of the direction of current in the circuit.
(iii) The change in potential in traversing a capacitor from the negative plate to the positive plate is + q/C while in opposite direction – .
(iv) The change in voltage in traversing an inductor in the direction of current is –L dl/dt while in opposite direction it is +L dl/dt.
Must Watch
Must Watch
- Video on Kirchhoff's Law
- Symmetry Analysis on Circuit Network
